Understanding what is a deductible in insurance is essential for managing your insurance costs and financial planning. An insurance deductible is the amount of money you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage begins to help with a claim. Whether you are dealing with health, home, or auto insurance, knowing what are insurance deductibles can help you make informed decisions, save on premiums, and choose the right coverage for your needs.
What Is a Deductible in Insurance
A deductible is the portion of a claim you agree to pay before your insurance coverage takes effect. It acts as a shared financial responsibility between you and your insurer. The deductible amount depends on your policy and can directly impact your premiums.
Simple Definition and How It Works
Consider a deductible as your initial contribution when something happens, like an accident or a medical expense. You cover this amount first, and then your insurance pays for the rest, up to the policy limit. This cost-sharing arrangement helps insurers keep premiums manageable while encouraging responsible claims.
For example, if your car repair costs $3,000 and your deductible is $500, you pay $500, and the insurer covers the remaining $2,500. Health insurance works similarly: you pay for medical expenses until your total out-of-pocket costs match your deductible amount. Once reached, your insurer begins covering a larger share of the costs, often through coinsurance.
Types of Insurance Deductibles
Deductibles vary based on the type of insurance policy you hold. Each type has its own rules and cost structures, so understanding these can help you make informed choices and avoid surprises when filing a claim.

Health Insurance Deductibles
Health insurance deductibles apply to medical expenses you incur before your plan’s coverage takes effect. There are two main types:
- Individual Deductible: Applies to one person on the plan and resets yearly.
- Family Deductible: Covers all members of a family plan and combines their medical expenses.
For instance, if your plan includes a $2,000 family deductible, all out-of-pocket costs for covered family members count toward that amount. Once the deductible is met, the insurer begins sharing costs for services like doctor visits, prescriptions, or hospital stays.
Car Insurance Deductibles
Car insurance deductibles apply when filing claims for vehicle-related damage. These are common for two types of coverage:
- Collision Coverage: Pays for repairs when your car collides with another vehicle or object.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers non-collision events like theft, vandalism, or weather-related damage.
If a tree falls on your car and the repair bill is $4,500, with a $1,000 comprehensive deductible, you pay the first $1,000, and your insurer covers the rest. Choosing a higher deductible lowers your premium but increases your financial risk when filing claims.
Home Insurance Deductibles
Home insurance deductibles apply to property-related claims, such as fire damage, theft, or natural disasters. Deductibles can come in two forms:
- Flat Deductibles: A fixed dollar amount, like $1,000 per claim.
- Percentage-Based Deductibles: A percentage of your home’s insured value, often for large claims like hurricane or earthquake damage.
For example, if your home is insured for $300,000 and you have a 2% hurricane deductible, you’ll pay $6,000 toward the claim before your insurance takes over.
High Deductible vs Low Deductible Plans
Choosing between a high deductible and a low deductible plan depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and insurance needs. Both options affect your premiums and out-of-pocket expenses in different ways. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each can help you make the right decision.
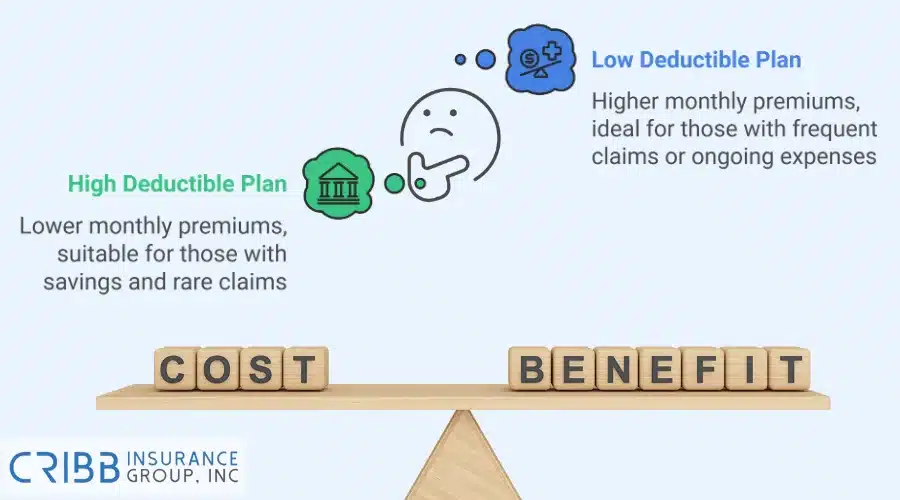
Pros and Cons of High Deductibles
High deductibles are common in insurance plans because they lower monthly premiums. However, they can create higher financial burdens when you file a claim.
Pros of High Deductibles | Cons of High Deductibles |
|---|---|
|
Lower monthly premiums, which can save money over time. |
Higher out-of-pocket costs if you need to file a claim. |
|
Ideal for those who rarely file claims or have emergency savings to cover higher costs. |
Risk of financial strain if you don’t have enough savings to cover the deductible. |
|
Encourages mindful use of insurance, especially for health plans. |
Not ideal for individuals with frequent medical needs or those who live in high-risk areas for accidents or property damage. |
For instance, a high-deductible health insurance plan may be cost-effective for young, healthy individuals who rarely visit the doctor. However, someone with ongoing medical expenses might find the out-of-pocket costs too high.
Pros and Cons of Low Deductibles
Low deductibles provide better financial protection when you file a claim, but they come with higher monthly premiums. This option is suitable for those who prefer predictability in their expenses.
Pros of Low Deductibles | Cons of Low Deductibles |
|---|---|
|
Lower out-of-pocket costs when filing a claim. |
Higher monthly or annual insurance premiums. |
|
Better financial protection for individuals with frequent claims or unexpected expenses. |
May not be cost-effective for individuals who rarely file claims. |
|
Reduced risk of financial stress during emergencies. |
Premium payments could add up to more than the deductible savings over time. |
For example, someone with a low deductible on their car insurance pays higher monthly premiums but benefits from smaller out-of-pocket costs when making a claim. This option works well for drivers in areas with high accident rates or those with older vehicles that may require frequent repairs.
How Deductibles Affect Insurance Premiums
Deductibles and premiums are closely connected. The deductible amount you choose directly impacts the cost of your monthly or annual insurance premium. Understanding this relationship can help you find a balance that aligns with your budget and financial goals.
Understanding the Relationship Between Costs
A deductible is the amount you agree to pay before your insurance starts covering a claim. The higher your deductible, the lower your premium will be. Insurers reward higher deductibles with lower premiums because it reduces the likelihood of frequent, small claims. Here is how the relationship works:
- Higher Deductible: Lowers the monthly or annual premium since you take on more financial risk when filing a claim.
- Lower Deductible: Increases the premium since the insurer covers more upfront costs for claims.
For example, car insurance with a $1,000 deductible costs less per month compared to a plan with a $500 deductible. The trade-off is that you will pay more out of pocket if you file a claim. Similarly, in health insurance, higher deductibles reduce premiums, but you shoulder more medical expenses before coverage begins.
How to Balance Premiums and Deductibles
Finding the right balance between premiums and deductibles involves considering your financial situation, risk tolerance, and coverage needs. Here are some tips to help:
- Assess Your Emergency Savings: If you have enough savings to cover a higher deductible, you can save on premiums by choosing a plan with a lower monthly cost.
- Consider Your Risk Level: People with frequent claims, such as those with ongoing medical needs or who live in high-risk areas, benefit from low deductibles despite the higher premiums.
- Evaluate Your Budget: Review your monthly expenses to determine how much you can afford in premiums versus how much you can handle in unexpected costs.
- Think About Claim Frequency: If you rarely file claims, a high-deductible plan may be more cost-effective over time.
For instance, someone who drives an older car with a high deductible pays less monthly, assuming repairs or accidents are unlikely. On the other hand, a family with frequent medical expenses benefits more from a low-deductible health insurance plan.
Balancing your deductible and premium ensures you aren’t overpaying while staying financially prepared for emergencies.
Misconceptions About Insurance Deductibles
Many people misunderstand how insurance deductibles work, which can lead to confusion when filing claims. Clearing up these misconceptions helps you make informed decisions and avoid surprises when handling out-of-pocket costs.

Do You Pay a Deductible Every Time
No, you don’t always pay a deductible for every claim or situation. Whether a deductible applies depends on the type of insurance policy and the specific coverage. Here’s how it works across common scenarios:
- Car Insurance: You pay a deductible for collision or comprehensive claims but not for liability coverage. Liability insurance covers damages to others, so no deductible applies.
- Health Insurance: A deductible applies to services like doctor visits, hospital stays, or procedures. However, preventive care under many health plans is often fully covered without requiring a deductible.
- Home Insurance: Deductibles apply to property damage claims, like fire or theft. However, they generally do not apply to liability claims if someone gets injured on your property.
Understanding when a deductible applies ensures you know what to expect when filing a claim. Policies vary, so always check your specific coverage terms.
Is a Deductible the Same as a Copay
No, a deductible and a copay are not the same, although both involve out-of-pocket costs. Here’s the difference between the two:
- Deductible: This is a fixed amount you must pay before your insurance begins to share costs. Once you reach the deductible, the insurer starts covering a percentage of expenses, often through coinsurance.
- Copay: This is a fixed fee you pay for specific services or prescriptions, regardless of whether you’ve met your deductible. Copays are usually smaller amounts, such as $20 for a doctor’s visit or $10 for a generic prescription.
For example, if your health insurance has a $1,000 deductible, you pay all costs until you reach that amount. After meeting the deductible, you might still pay a $20 copay for doctor visits. Copays remain constant, while deductibles represent the upfront costs before coverage applies.
Knowing the difference between a deductible and a copay helps you plan for medical expenses and understand how your health insurance policy works.
How to Choose the Right Deductible for Your Needs
Choosing the right deductible requires careful consideration of your financial situation, insurance needs, and risk tolerance. A deductible that works for one person may not suit another, so understanding what impacts your choice can help you make the best decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Deductible
Selecting the right deductible comes down to balancing upfront costs with long-term savings. Here are the key factors to keep in mind:
- Emergency Savings: Determine how much you can afford to pay out of pocket in case of a claim. If you have enough savings, a higher deductible can reduce monthly premiums.
- Monthly Budget: Review your monthly expenses to ensure you can handle the premium associated with a low or high-deductible plan.
- Claim Frequency: If you rarely file claims, a high deductible plan may save you money. Frequent claims make a low deductible more cost-effective.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your comfort level with financial risk. Higher deductibles mean lower premiums but greater out-of-pocket costs during a claim.
- Policy Type: Different policies, like car, health, or home insurance, have varying deductible structures. For example, a percentage-based deductible in home insurance might cost more for high-value properties.
By considering these factors, you can choose a deductible that aligns with your financial goals while ensuring you are protected when unexpected costs arise.

Tips for Staying Prepared for Out-of-Pocket Costs
Being prepared for deductible payments can reduce financial stress when filing a claim. Here are practical tips to help you stay ready for out-of-pocket expenses:
- Build an Emergency Fund: Set aside savings specifically for insurance deductibles. Aim to save at least the amount of your highest deductible across all policies.
- Review Your Policy Annually: As your financial situation changes, reassess your deductible and premium to ensure they still work for you.
- Budget for Deductible Costs: If you choose a high deductible, factor it into your budget. Treat it as a mandatory expense you need to cover in case of an emergency.
- Know Your Coverage: Understand what types of claims require a deductible and what costs are covered by your policy. This prevents surprises during claims.
- Plan for Specific Risks: If you live in a high-risk area, like flood-prone regions or hurricane zones, plan for deductibles specific to those events.
Staying financially prepared for out-of-pocket costs ensures you can handle claims quickly and smoothly without disrupting your budget or long-term savings.
Making the Right Insurance Deductible Choice
Choosing the right insurance deductible can make a significant difference in how much you pay for premiums and claims. At Cribb Insurance Group Inc, we understand that insurance can feel overwhelming. Whether you need coverage for your car, home, or health, knowing what is a deductible in insurance helps you make confident decisions that fit your financial needs.
Cribb Insurance Group Inc offers tailored solutions to help you navigate your options and select the deductible that works for you. For residents of Bentonville, AR, our team ensures you get clear, honest guidance on managing your premiums, deductibles, and coverage effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a deductible differ from an out-of-pocket maximum?
A deductible is the amount you pay before your insurance starts covering expenses. An out-of-pocket maximum is the most you’ll pay in a year, including deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of additional costs for the rest of the year.
Can I change my deductible after purchasing insurance?
Yes, you can usually change your deductible, but it depends on your insurance provider and policy. Some insurers allow adjustments at any time, while others require you to wait until the policy renewal period. Always check with your provider to understand the rules.
What happens if I cannot afford to pay my deductible?
If you can’t pay your deductible, your claim may remain unpaid until you cover the amount. Some insurers offer payment plans to help spread the cost. Building an emergency fund in advance can prevent this issue and ensure you get the coverage you need.
Are deductibles the same for all insurance policies?
No, deductibles vary depending on the type of insurance. For example, car insurance has deductibles for collision and comprehensive claims, while health insurance deductibles apply to medical services. Policies like home insurance may also use percentage-based deductibles for certain claims.
How does a zero-deductible insurance plan work?
A zero-deductible plan means you don’t pay any out-of-pocket costs before your insurance kicks in. While this eliminates upfront expenses, it typically comes with higher monthly premiums. Zero-deductible plans are ideal for those who prefer predictable costs over lower premiums.
Talk to Cribb Insurance Group Inc Today
For reliable insurance solutions in Bentonville, AR, call Cribb Insurance Group Inc at (479) 286-1066. Let our team help you understand your options and choose the right insurance deductible for your needs. Protect your finances with coverage you can trust.





